Three building condition zones are defined within the E.P.S urban planning unit.
Zone Α.
- Housing for park workers.
- Education. Only higher education with the function of a Higher Education institution is allowed
- of (A.E.I.).
- Administration.
- Trade and provision of personal services.
- Offices/Research Centers/Business Incubators.
- Focus.
- Refreshments.
- Parking (buildings and courts) of cars up to 3.5 tons for shared use, motorcycles and mopeds.
- Warehouses (low nuisance).
- Professional workshops
- Industrial and low-noise industrial facilities. Uses refer to units
- of highly advanced technology (biotechnology, informatics, microelectronics, etc.) and are developed at a rate of at least 60% of the total area of the receptor/park.
- Green points.
- Wastewater treatment and disposal area.
- Installations of Renewable Energy Sources (A.P.E.).
- Public gathering places - conference centers
Zone Β.
- Residence.
- Small and special sports facilities.
- Religious places.
- special tourist infrastructure facilities and other tourist businesses.
- parking spaces
- Open Spaces - Urban Green.
- Cultural facilities.
- Venues/Conference Centres.
- Trade and provision of personal services.
- Offices - research centers - business incubators.
- Focus.
- Refreshments.
- Recreation.
- Tourist accommodation
Zone C.
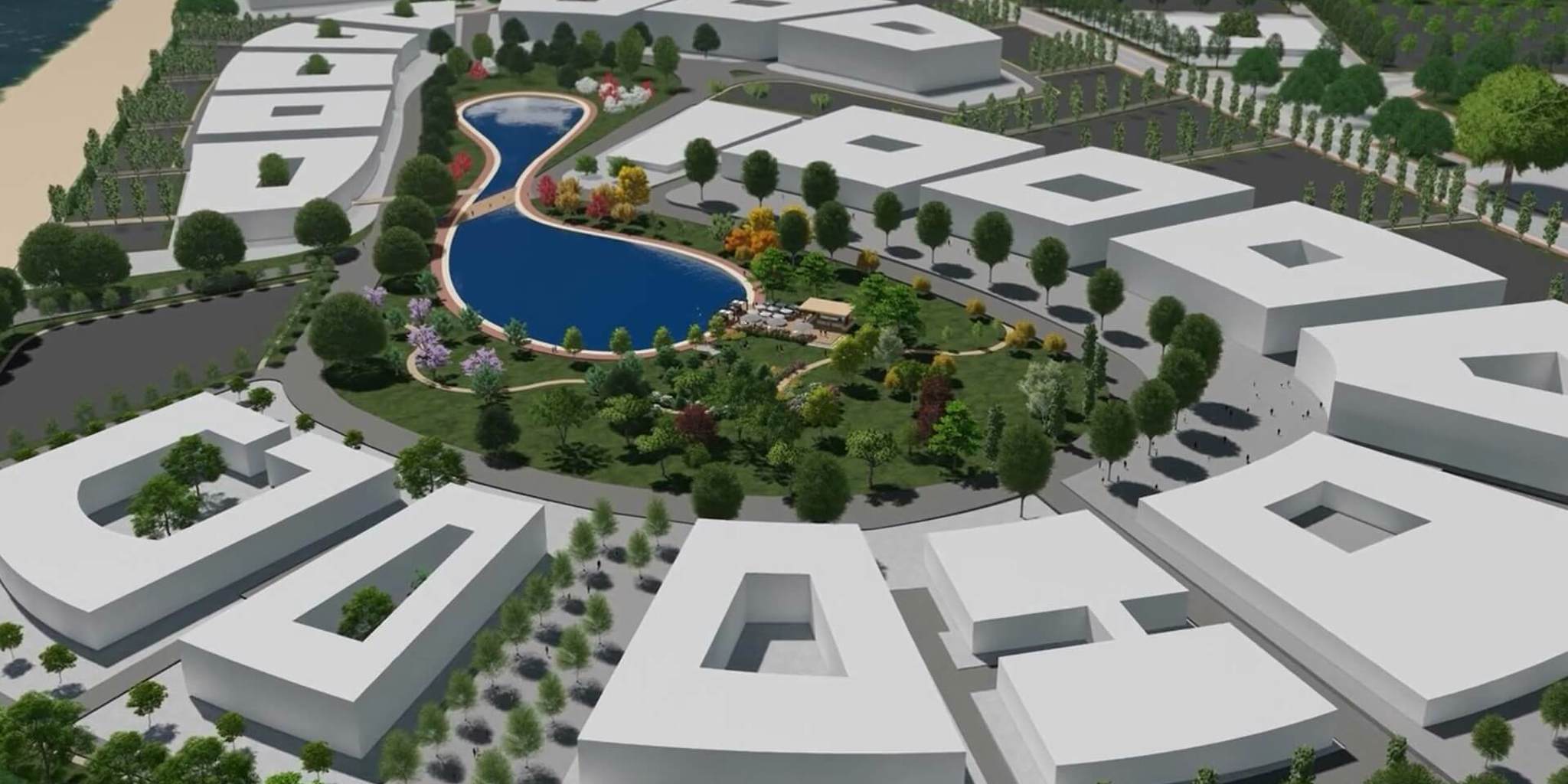
- In Zone C, an urban green space is intended for the common green area zone that runs along the property's northern coast.
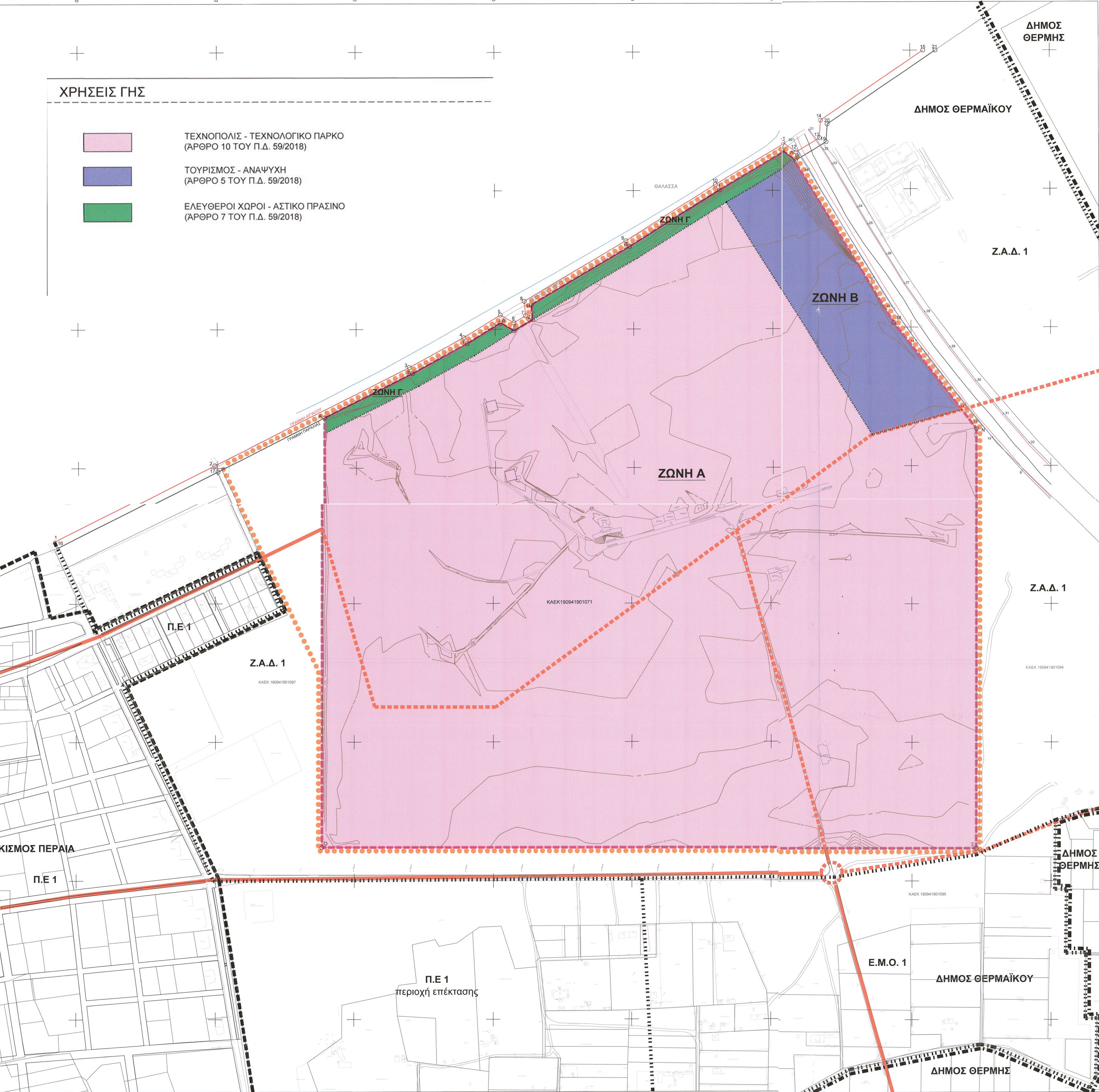
An average building factor of 0.45, which is equivalent to about 340,000 square meters, has been determined for the entire intervention area. Out of this, 230,000 square meters are intended for R&D labs and offices. The percentage of common and public spaces is equal to 25% of the total surface area, out of which at least 90 acres is reserved for serving needs on a supra-local scale.
The park will be developed in four phases
In "Phase A", the development of utility and network infrastructure, along with essential building facilities for high-tech companies, startups and research institutions will be completed. The total budget for "Phase A" is estimated to be 70 million euros plus VAT (24%). This budget includes the infrastructure of the entire property and construction of approximately 10% of the total construction of the project (BUA).
The remaining 90% of the buildings in the park will be constructed in Phases B, C, and D.
It is important to note that 40% of the buildable area of the park has been granted to the Israeli fund JLTV and the Beersheva Technology Park. The Israeli fund will transfer valuable know-how while its infrastructure within "Thess INTEC" will be developed by the National Center for Research and Technological Development (ETEKA).
During the first phase of the project, 50 million euros will be invested in infrastructure and the first buildings. An additional investment of 25 million euros from EKETA and 30 million euros from the Israeli Fund is also expected. Over a period of ten years, the total investments are projected to exceed 500 million euros.
"Thess INTEC S.A. Science & Technology Park Development Company" is a non-profit organization with 58% of its shares owned by the private sector (7 members of the Board of Directors) and 42% by the public sector (4 members of the Board of Directors).
The implementing body's shareholders include three universities, the EKETA Research Center, public and private sector bodies. The project is supported during its maturation stage through S.A. non-profit by a total of 25 flagship companies/sponsors.